The link between the gut microbiome—the microorganisms living inside our bodies—and various diseases has already been proven through numerous research findings.
Recently, it has been reported that combining the microbiome with medical AI can enable early diagnosis of liver disease and even lead to the development of treatments for conditions such as muscle loss.
Reporter Kim Seon-yeop reports.
<Reporter>
The gut microbiome not only measures the state of gut health, but its associations with a wide range of conditions that occur in our bodies—such as obesity, cancer, and depression—are also being identified.
As a result, cases of using the microbiome for early disease diagnosis and even the development of personalized therapeutics are increasing significantly.
In particular, to properly understand the habitat environment and balance state of the microbiome—numbering in the tens of trillions within the human body—the role of AI, which learns from big data, is essential above all.
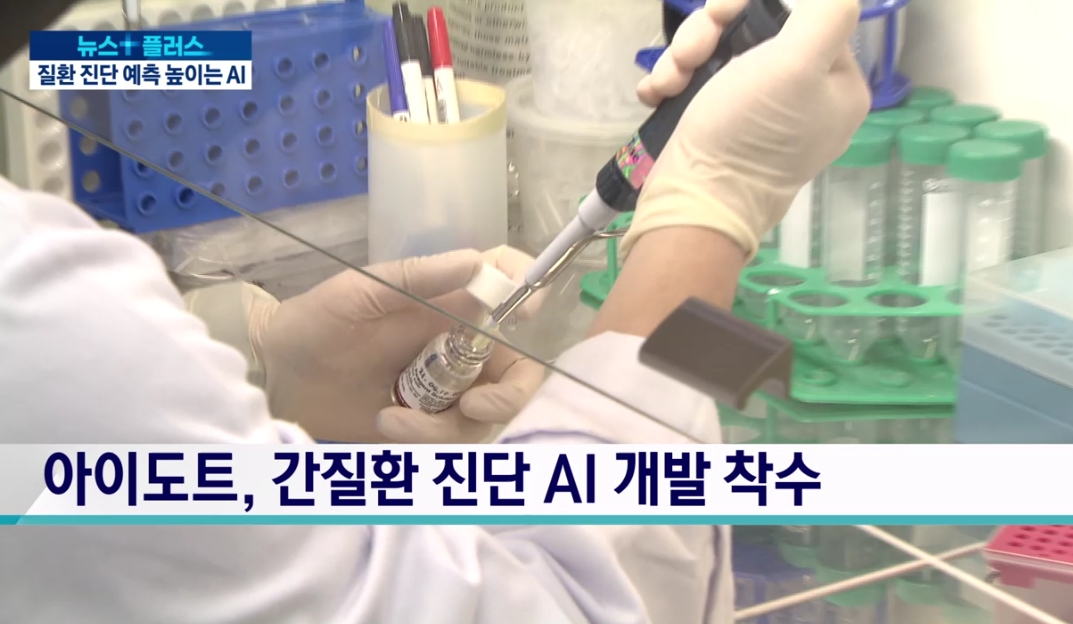
In Gangwon Province, recently designated as a precision medicine big data special zone, medical AI company AIDOT has entered the microbiome business together with Hallym University Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital.
They have begun R&D on an AI microbiome solution that early-diagnoses liver disease through a simple stool test.
The principle is to combine microbiome research results with next-generation sequencing (NGS) to identify alcoholic liver disease, and then apply that to an AI algorithm.
[Seok Ki-tae / Professor, Division of Gastroenterology, Hallym University Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital: People with liver cirrhosis, those with hepatitis, and those with other liver diseases each have disease-specific characteristic findings. We thought that if we develop an (AI solution) by measuring the microbiome’s distribution or the domain of pathogenic strains like these to diagnose disease, it could help with liver disease diagnosis—so we proceeded with this main research.]
AIDOT’s AI solution, trained on microbiome big data from 1,800 liver disease patients, diagnoses abnormalities by classifying liver status into four stages: normal (fatty liver), hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
For liver disease diagnosis, MRI testing has low sensitivity, so invasive biopsies also have to be performed. Diagnosis using AI, the explanation goes, overcomes these shortcomings.
[Jeong Jae-hoon / CEO, AIDOT: If we find biomarkers through the microbiome and conduct screening through microbial genome analysis of stool, we are currently aiming for over 80% sensitivity. (Then) there’s no need to take risks anymore.]
AIDOT plans to commercialize the solution within two years.
BioLeaders, which is working to develop a treatment for age-related sarcopenia using AI and the microbiome, is also drawing attention.
The approach is to use AI to express antigen proteins myostatin and activin on the microbiome surface, thereby removing substances that cause age-related sarcopenia.
[Lee Do-young / Managing Director, Clinical Development Center, BioLeaders: In age-related sarcopenia, knowing which proteins to target is the most important part of developing a treatment. There are many literature materials on sarcopenia, but we used AI to simulate which combination of targets would be most effective. In that process, we concluded that simultaneously targeting two proteins is most effective, and that’s why we proceeded with drug development.]
As AI is added to the microbiome, expectations are growing for the diagnosis of various diseases and the development of therapeutics using this foundational technology.
Published: December 17, 2021 / Korea Economic TV / Reporter Kim Seon-yeop